In the United Kingdom the currency is made up of pound (£) and pence (p). There are eight coins in general circulation:
1p, 2p, 5p, 10p, 20p, 50p, £1 (100p), and £2 (200p). It is possible to make £2 in the following way:
1×£1 + 1×50p + 2×20p + 1×5p + 1×2p + 3×1p How many different ways can £2 be made using any number of coins?
硬币求和
英国的货币单位分为英镑(£)和便士(p)。目前流通的硬币一共有八种面值:
1p, 2p, 5p, 10p, 20p, 50p, £1 (100p), and £2 (200p).
想要凑出 £2,其中一种做法是:
1×£1 + 1×50p + 2×20p + 1×5p + 1×2p + 3×1p
不限制硬币数量,凑出 £2 有多少种不同的做法?
这样的问题还有多种描述方式,例如:现在有一个 200 级的台阶,我们现在可以一次上 1,2,5,10,20,50,100,200 级,那么总共有多少种方式能让我们上楼?再抽象一点,我们有 1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 200,如何选取数字让它们的和等于 200。
(当然,上楼梯和取钱不等价,上楼梯还要考虑顺序)
我们将这个数字集合叫做 \(S\),那么问题可以表述为 \((200, S)\),当我们向前一步后,一个问题可以变成 8 个问题:
- \((199, S), (198, S), (195, S), (190, S)\)
- \((180, S), (150, S), (100, S), (0, S)\)
从上面这 7 个(有一个已经到达 0 了)问题中的任何一个我们都可以衍生出 8 个问题,然后如此反复下去,遇到 0 就表示得到了一个解。将所有能到达 0 的路径加起来,我们就得到了这个问题的结果:
(defun eu31-coin (n S)
(cond ((= n 0) 1)
((< n 0) 0)
(t
(cl-loop for a in S
sum (eu31-coin (- n a) S)))))
(eu31-coin 4 '(1 2)) => 5当然,上面的结果是错的,应该只有下面这三种:
- 1 1 1 1
- 1 1 2
- 2 2
出现这样的错误原因也很简单,上楼梯是有顺序的但是钱与钱之间没有顺序,在我们的函数中计入了数量相同的不同组合,即 112,121 和 211。如果我们让结果总是有序的话就能够去除这些重复项:
(defun eu31-coin2 (n S)
(cond ((= n 0) 1)
(t (let ((res 0))
(while (and S (>= n (car S)))
(cl-incf res (eu31-coin2
(- n (car S)) S))
(setq S (cdr S)))
res))))
(my-time
(eu31-coin2 200 '(1 2 5 10 20 50 100 200)))
;;0.8772158622741699s
=> 73682我们可以把运算结果记在哈希表或数组里面,在运算时发现了相同项则可直接使用:
(defun eu31-coin3 (n S hash)
(cond
((= n 0) 1)
((gethash (cons n (car S)) hash))
(t
(puthash (cons n (car S))
(let ((res 0))
(while (and S (>= n (car S)))
(cl-incf res (eu31-coin3
(- n (car S)) S hash))
(setq S (cdr S)))
res)
hash))))
(my-time
(let ((hash (make-hash-table :size 1000 :test 'equal)))
(eu31-coin3 200 '(1 2 5 10 20 50 100 200) hash)
(cons (gethash '(200 . 1) hash) (hash-table-count hash))))
;;0.0075490474700927734s
=> (73682 . 1213)使用递归方法当然能解决问题,但是可能会爆栈。让我们再描述一下这个问题,现在由于要考虑到顺序,我们现在还需要一个用来表示可用元素的起始下标: \((S = [1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 200])\)
- 求 200 从 1 开始的组合: \((200, S_0)\)
- 求 5 从 5 开始的组合: \((5, S_2)\)
使用递归求取的问题在于它可能会重复求取某个 \((X, S_n)\),比如在我们计算 \((5, S_0)\) 时产生的递归树如下:
(5, 0) => (4, 0) + (3, 1) + (0, 2)
(4, 0) => (3, 0) + (2, 1)
(3, 1) => (1, 1)
(0, 2) => 1
(3, 0) => (2, 0) + (1, 1)
(2, 1) => (0, 1)
(1, 1) => 0
(2, 0) => (1, 0) + (0, 1)
(1, 1) => 0
(0, 1) => 0
(1, 0) => 1
(0, 1) => 0在这个计算中,出现重复的只有 \((1, S_1), (0, S_1)\) ,但是随着计算规模的增大,这样的重复也将越来越多。因此,我们可以考虑从后往前算,这样能确保每个 \((X, S_n)\) 只算一遍:
(my-time
(let ((tbl (make-vector 201 nil))
(coin [1 2 5 10 20 50 100 200]))
(dotimes (i 201) (aset tbl i (make-vector 8 0)))
(cl-loop for k from 0 below 8
do (aset (aref tbl 0) k 1)) ; (0, x) = 1
(cl-loop for i from 1 to 200
do (cl-loop for j from 0 below 8
do (aset (aref tbl i) j
(cl-loop for k from j below 8
for co = (aref coin k)
if (>= i co)
sum (aref (aref tbl (- i co)) k)))))
(aref (aref tbl 200) 0)))
;;0.006701946258544922s
=> 73682在上一节中我们完成了递归和动态规划的解法,不过在读完问题讨论区与问题的文档后我发现我的思路有些小问题。我对硬币的选取是从小面额到大面额,但更好的办法可能是反过来,从大面额到小面额(笑):
\[S = [200, 100, 50, 20, 10, 5, 2, 1]\]
\[(X, S_n) = \left\{\begin{align}&1 \ \ &if\ n = 7 \ \ \lor \ X = 0 \notag \\ \sum_{i=0}^{\lfloor\frac{X}{S_n}\rfloor}(X - &iS_n, S_{n+1}) \ \ &if\ n \lt 7\ \land \ X\ \gt 0 \notag \end{align}\right.\]
(defun eu31-a-coin (n S)
(cond
((= (car S) 1) 1)
(t (let ((res 0))
(while (> n 0)
(cl-incf res
(eu31-a-coin n (cdr S)))
(cl-decf n (car S)))
(when (= n 0) (cl-incf res))
res))))
(my-time
(eu31-a-coin 200 '(200 100 50 20 10 5 2 1)))
;;0.031058073043823242s
=> 73682下面是增加记忆后的版本:
(defun eu31-a-coin2 (n S idx tbl)
(cond
((= idx 7) 1)
((aref (aref tbl n) idx))
(t (let ((res 0)
(tn n))
(while (> n 0)
(cl-incf res (eu31-a-coin2 n (cdr S) (1+ idx) tbl))
(cl-decf n (car S)))
(when (= n 0) (cl-incf res))
(aset (aref tbl tn) idx res)
res))))
(my-time
(let ((tbl (make-vector 201 nil)))
(dotimes (i 201) (aset tbl i (make-vector 8 nil)))
(eu31-a-coin2 200 '(200 100 50 20 10 5 2 1) 0 tbl)))
;;0.003963947296142578s
=> 73682以下是可用于动态规划的公式:
\[(X, S_n) = \left\{\begin{align} &1 &if\ \ n = 7 \lor X = 0 \notag \\ (X, &S_{n+1}) &if\ \ n \lt 7 \land X \lt S_n \notag\\ (X, S_{n+1}) &+ (X - S_n, S_n) \ \ &if\ \ n \lt 7 \land X \ge S_n\notag\\ \end{align}\right.\]
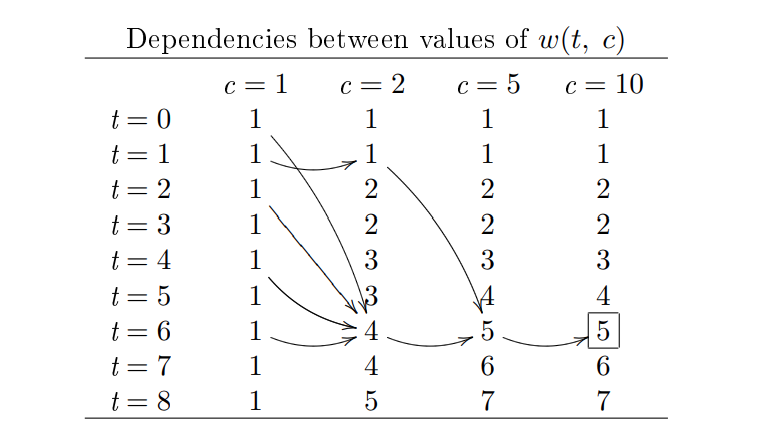
(my-time
(let ((tbl (make-vector 201 nil))
(S [200 100 50 20 10 5 2 1]))
(dotimes (i 201) (aset tbl i (make-vector 8 0)))
(cl-loop for i from 0 to 200
do (aset (aref tbl i) 7 1))
(cl-loop for i from 0 to 7
do (progn (aset (aref tbl 0) i 1)
(aset (aref tbl 1) i 1)))
(cl-loop for i from 2 to 200
do (cl-loop for j from 7 downto 0
do (aset (aref tbl i) j
(cond
((= j 7) 1)
((< i (aref S j))
(aref (aref tbl i) (1+ j)))
(t (+ (aref (aref tbl i) (1+ j))
(aref (aref tbl (- i (aref S j))) j)))))))
(aref (aref tbl 200) 0)))
;;0.0026040077209472656s
=> 73682当然,如果我们能注意到以下转移方式,我们只需要上面 1/8 的空间即可完成:
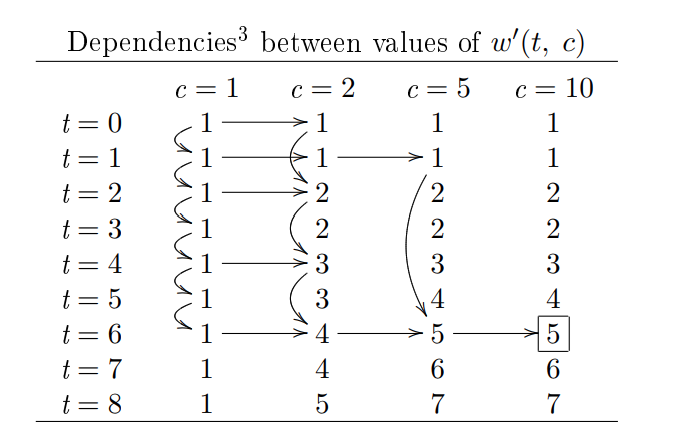
(my-time
(let ((tbl (make-vector 201 0))
(S [1 2 5 10 20 50 100 200]))
(aset tbl 0 1)
(cl-do ((i 0 (1+ i))) ((= i 7))
(cl-do ((j (aref S i) (1+ j))) ((> j 200))
(cl-incf (aref tbl j) (aref tbl (- j (aref S i))))))
(aref tbl 200)))
;;0.0019969940185546875s
=> 73681请参考题解的 overflow 文档来详细了解。